Chapter 6. Segmentation
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in the Pro edition
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Segmentation is the division of an object into its component parts to facilitate research and modelling.
The tasks that segmentation solves:
-
researching separate tissue parts with a certain density range. Usually, such parts have a complicated form and are hidden inside other tissues, hence it is impossible or difficult to highlight them with the cutting tools, e.g.: teeth and thir roots, tumors, bones, vessels;
-
calculating the volume of tissue, such as tumors;
-
studing mutual disposition of tissues that can notbe visible simultaneously;
-
fusing a segment and a whole model to see its location within the tissue;
-
exporting the structure surface for further use, such as 3D-printing;
-
importing the objects used in the treatment to simulate their location in the tissues;
-
dividing tissues into separate fragments for better visualization.
-
cutting tissue by a mask created from a segmented structure.
To solve these problems, the DICOM Viewer allows you to build segmented structures both automatically and manually.
The segmentation of tissues is possible in the Volume Reconstruction window and the Multiplanar Reconstructions window. In both modes you work with the same segmented structure (structures), thereby for its/their construction you can use the benefits of both modes, switching between them.
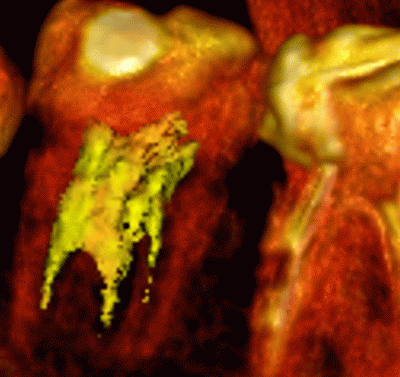
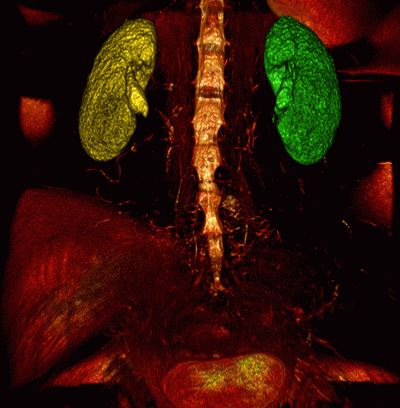
Fig. 6.1 illustrates the segmented root of a tooth hightlighted in yellow. Fig. 6.2 illustrates segmented kidneys highlighted in red and blue. The base volume is highlighted with the CLUT so that the bones can be seen best and the other organs are not visible.
6.2 The Mask
6.2.1 Creating a new structure and mask
6.2.2 Changing the structure mask using CLUTs
6.2.3 The Editing mask
6.2.4 Set Mask Tool
6.3 Creating segmented structure
6.3.1 Creating a structure by copying
6.3.2 Creating a Structure with a Empty Mask
6.4 Actions with structure
6.5 Building surface
6.6 Copying a Surface
6.7 Import and Export
6.7.1 Export surface
6.7.2 Import surface
6.7.3 Export a structure to the current study
6.7.4 Export a structure to DICOM RT
6.7.5 Importing a Structure from DICOM RT
6.8 Changing the structure mask with segmentation tools
6.8.1 Tools for automatic segmented structure mask filling
6.8.2 Brush restore tool
6.8.3 Region growing tool
6.8.4 Vessel tree segmentation tool
6.8.5 Watershed segmentation tool
6.8.6 Multi-segment growing tool
6.8.7 Segmented structures regions growing Tool
6.9 Union, subtraction and intersection of structures
6.9.1 Union
6.9.2 Subtraction
6.9.3 Intersection
6.9.4 "Subtract dilated" Tool
6.10 Building Mask with Contours
6.10.1 General Information
6.10.2 Building a Structure Mask with Contours
6.10.3 Work with Contours
6.10.4 Setting the Contour Display Parameters
6.11 Saving and Opening Segmentation Projects and DTI Projects
6.11.1 Saving a Project
6.11.2 Saving Projects Automatically
6.11.3 Resuming Work with Segmentation Projects
6.11.4 Opening a Project with Source DICOM Data
6.11.5 Opening a Project without Source DICOM Data
6.12 Histograms
6.12.1 Rendering a Histogram for a Structure
6.12.2 Histogram for a ROI