15.3. Burn image
If you need to write a DICOMDIR file to a disk (memory card), enable the corresponding option in the Dick Creator settings dialog (see Section 16.7.7).
Data burning may fail for some models of CD/DVD-ROMs. To increase the reliability of recording enable image buffering (see Section 16.7.7). In this case, the buffer file for writing is created entirely in the temporary folder of the current user just before writing to disk. Buffer files are created before each recording and are deleted from the hard disk only when the DICOM Viewer is closed. Hence, the amount of free space on the hard disk should be taken into account when writing to the disk multiple times within one session of the program.
15.3.1 Write to Disk
 | Attention! In Linux and macOS you can write data to a memory card or burn a disk image created in the Work Folder to a disk, using the operating system tools. |
More detailed information in the Section 15.3.3.
To write information to a disk:
-
Click the Burn created DICOM CD/DVD image to the optical disk
 button
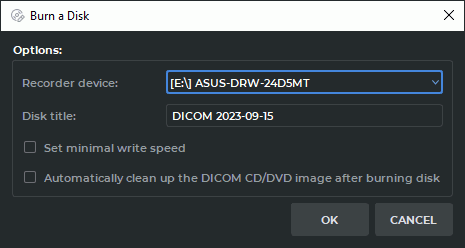
on the Disk Creator toolbar. The window shown in Fig. 15.3 will pop up.
button
on the Disk Creator toolbar. The window shown in Fig. 15.3 will pop up.
-
If necessary, select the recorder device from the dropdown menu.
-
Edit the disk name if necessary.
-
If necessary, check/uncheck the Set minimal write speed box.
-
If necessary, check/uncheck the Automatically clean up the DICOM CD/DVD image after burning disk box.
-
Click OK to write or CANCEL to cancel.
If the Automatically clean up the DICOM CD/DVD image after burning disk box is checked, the information stored in the Work Folder of the creator will be deleted. Otherwise you will be able to record it again.
15.3.2 Write to Memory Card or Folder
To write information to a memory card (flash card) or folder:
-
Click the Write created DICOM CD/DVD image to the flash card or folder
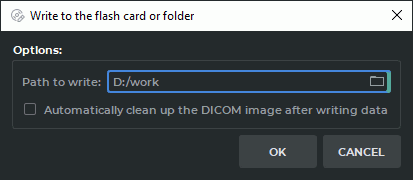
 button on the Disk Creator toolbar. Dialog box is swown in Figure 15.4.
button on the Disk Creator toolbar. Dialog box is swown in Figure 15.4.
-
Select a memory card or folder on your hard disk. To do this, enter the path in the Path to write field or click the
 button and select the path in the dialog that
opens.
button and select the path in the dialog that
opens.
-
If necessary, check/uncheck the box Automatically clean up the DICOM CD/DVD image after writing data.
-
Click OK to write or CANCEL to cancel.
15.3.3 Burn an image to CD / DVD in Linux and macOS operating systems
To write information to a disk:
-
The Work Folder should be created, i.e. the folder to store the disk image to be written.
-
Save the information to the created directory, in accordance with the Section 15.3.2.
-
Burn a disk image created in the Work Folder to a CD/DVD using the operating system tools or special applications.