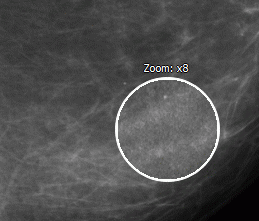
Activate the Magnifier  tool on the toolbar by clicking the left/right/middle mouse
button. To continue work with this tool, use the button with which the tool was activated.
To learn more about tool control, see Section 1.14.
tool on the toolbar by clicking the left/right/middle mouse
button. To continue work with this tool, use the button with which the tool was activated.
To learn more about tool control, see Section 1.14.
Move the cursor to the area you want to make out.
To increase the value of the zoom increment, click the mouse button with which the tool was activated. To reduce value, click the mouse button with which the tool was activated holding down the Alt key (or the Option key for macOS) on the keyboard.
The radius and the zoom increment of the tool are set in the Magnifier options dialog
box. To set these parameters, click on the arrow on the right side of the  button
and select Options...
button
and select Options...