8.1 Cardiac function analysis mode
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
8.1.1 Opening Studies for the Cardiac function analysis
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
To open a study for the cardiac function analysis, proceed as follows:
-
Choose a study and select MR series with images oriented along the short and long axis
of the heart.In some cases, you don’t have to select series with images oriented along the
long axis of the heart. For details on selecting series, see Section 1.10.
-
Click the Cardiac analysis  button on the toolbar. To select the tab location (in
the current window, in a separate window, or in the full-screen mode), press the arrow
on the right-hand side of the button. To open the cardiac analysis window in a new tab
in the current window, press the button. The process may take some time.
button on the toolbar. To select the tab location (in
the current window, in a separate window, or in the full-screen mode), press the arrow
on the right-hand side of the button. To open the cardiac analysis window in a new tab
in the current window, press the button. The process may take some time.
The Cardiac analysis tool is also available in the View section of the main menu.
-
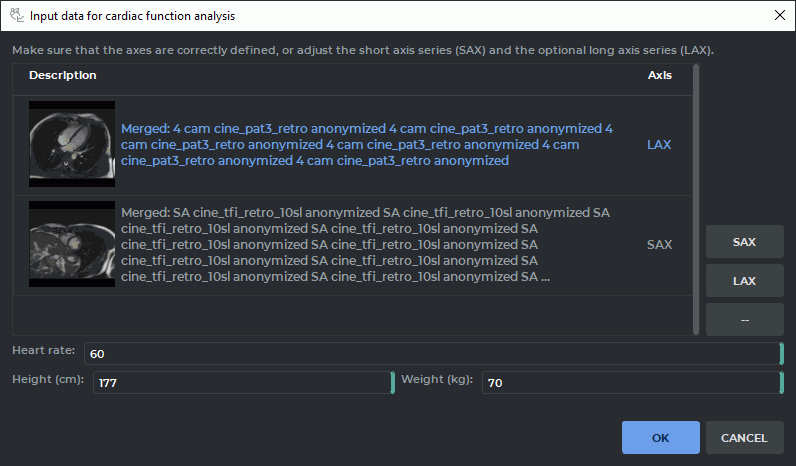
When the cardiac analysis module is activated, the Input data for cardiac analysis
dialog box pops up (see Fig. 8.1). From the drop-down list, select the Function analysis
mode. This mode provides for analysis and evaluation of cardiac functional parameters.
The T1 analysis mode provides an opportunity to create a map showing the T1
relaxation time for quantification of changes in the cardiac tissue. For details on this
mode, see Section 8.2.1.
In theFunction analysis mode, the DICOM Viewer automatically arranges the selected
series in groups. A group consists of one or several series united by planes parallelism.
If there is more than one series in a group, series are merged. For each series group, the
type is automatically defined: with images oriented along the short axis of the heart SAX
(Short axis series) or with images oriented along the long axis of the heart LAX (Long
axis series). Sometimes the series type cannot be defined automatically. In this case, you
will see the — symbol as the axis type.
 | If
the
series
to
be
merged
have
the
same
names,
a
suffix
(xN)
will
be
added
to
the
merged
series
description
for
each
group
of
series
with
the
same
names,
where
N
stands
for
the
number
of
series
with
the
same
names. |
The user may change the type of axis for the group. To do that, select the group and click
the Set as SAX or Set as LAX button. You don’t need the series with images
oriented along the long axis of the heart (LAX) series to analyze certain cardiac
functions.
To reset the type of axis for the group, select it on the list and click Reset selected
series — .
 | To
continue
work,
you
need
at
least
one
series
or
group
to
have
the
SAX
type
of
axis. |
-
In the lower part of the dialog box, you can see the information about the patient
that is loaded automatically. Sometimes only a part of the information is filled in
automatically. In this case, other parameters referring to the patient must be provided
manually:
-
heart rate (beats/min);
-
height (cm);
-
weight (kg).
-
Click OK to enter the data required for cardiac function analysis or CANCEL to
cancel.
If you haven’t provided all the required parameters in the Input data for cardiac analysis
dialog box (see Fig. 8.1), the OK button will be deactivated.
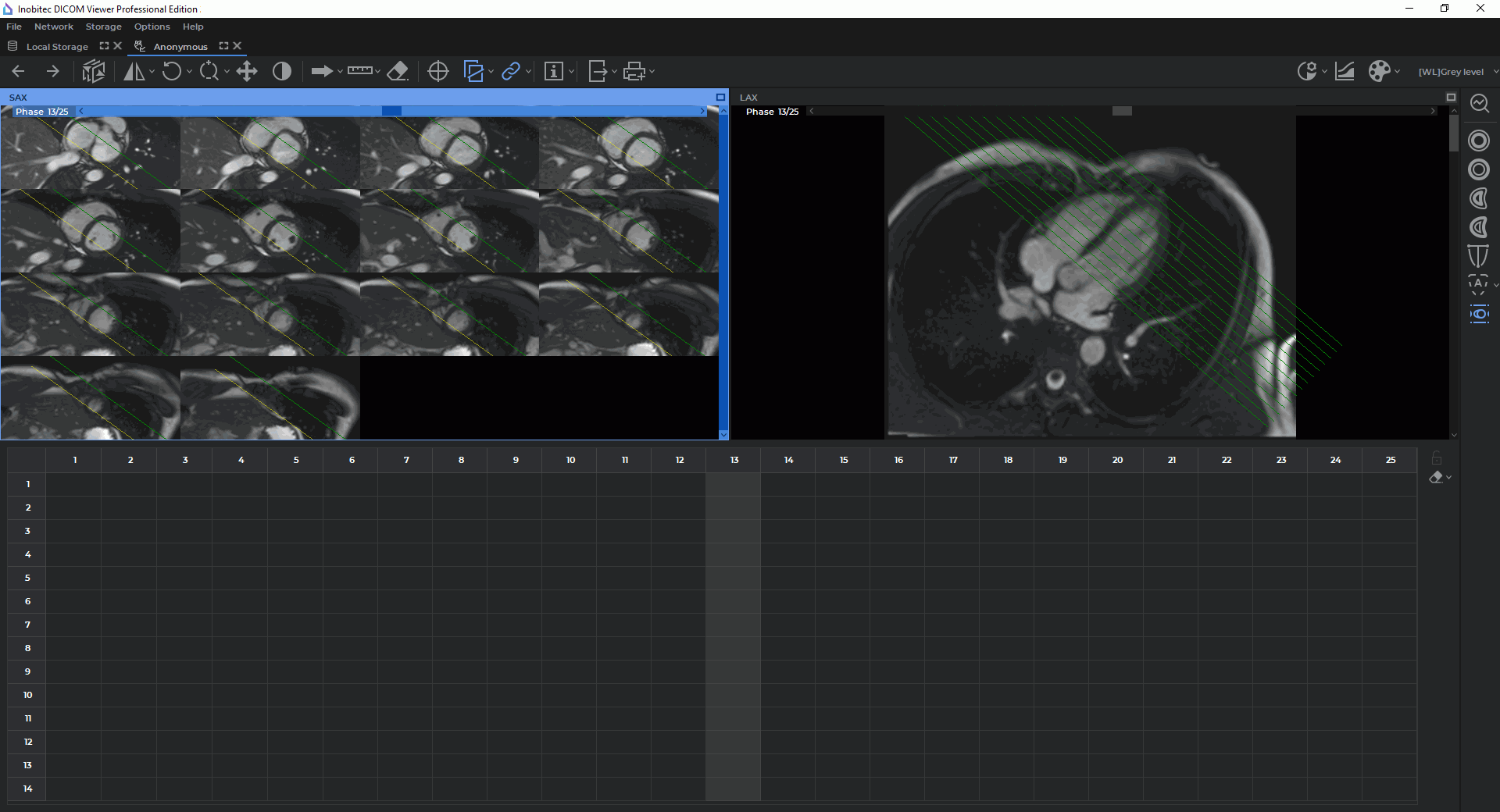
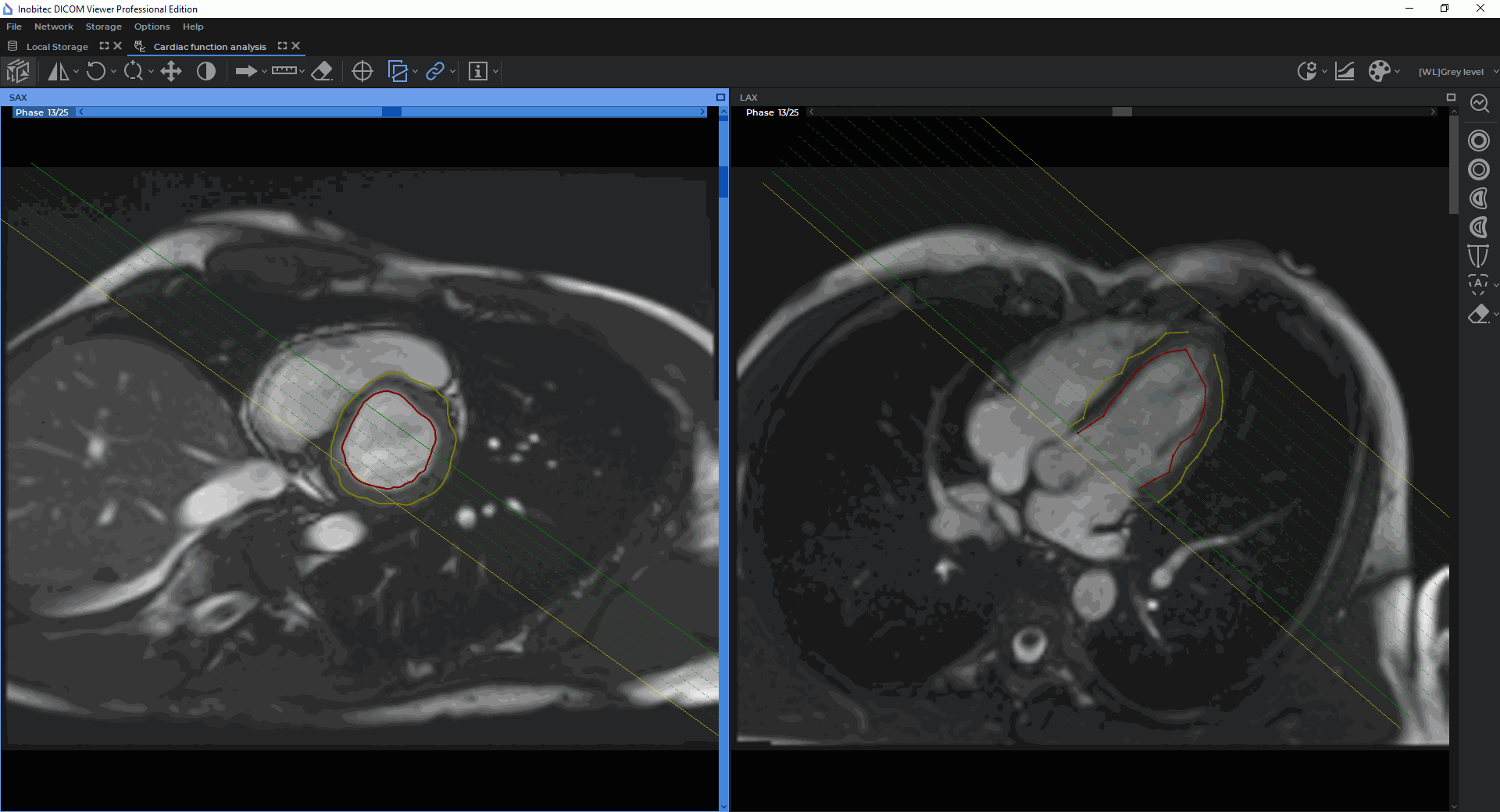
In the Cardiac analysis tab, you can see two windows, with the SAX merged series and the LAX
merged series (Fig. 8.2). The toolbar for cardiac function analysis is on the right-hand side of the
tab.
Under the SAX and LAX windows, you can see the contours panel aimed for navigation between
images and contour management (for details see Section 8.1.7). By default, the panel is
expanded.
By default, all the slices for the current phase are shown in the SAX window. The phases may be
switched by moving the slider along the horizontal scroll bar at the top of the SAX window or on the
contour panel.
To escape the mode displaying all the slices for the current phase, click the right mouse button in
the SAX window and disable the Multi-SAX arrangement option on the context menu. By
default, the option is enabled and highlighted with blue on the menu. The SAX window in the
Cardiac analysis tab will be displayed as shown in Fig. 8.3.
In this particular case, the SAX window shows only one slice for the current phase. The slices may
be switched by moving the slider along the vertical scroll bar on the right-hand side of the window or
on the contour panel.
To go back to the mode displaying all the slices for the current phase, click the right mouse button
in the SAX window and enable the Multi-SAX arrangement option on the context
menu.
 | If
only
one
slice
is
displayed
in
the
SAX
window,
the
Multi-SAX
arrangement
option
is
unavailable. |
After the slices are moved or scaled, their arrangement in the SAX window can be optimized. To
do this, click the right mouse button in the SAX window and select the Apply auto
transform option on the context menu. The slices arrangement in the SAX window will be
optimized: the empty space will be minimized, and the heart will occupy the optimal
position.
 | Slices
arrangement
optimization
in
the
SAX
window
is
applied
by
default
when
the
Cardiac
analysis
tab
is
opened. |
8.1.2 Tools for Cardiac Function Analysis
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
The toolbar for cardiac function analysis is on the right-hand side of the Cardiac analysis
(Fig. 8.3).
Tools:
 | The
Endocardial
LV
contour
button
is
aimed
for
building
and
editing
the
inner
contour
of
the
left
ventricle
manually
(the
contour
is
shown
in
red) |
 | The
Epicardial
LV
contour
button
is
aimed
for
building
and
editing
the
outer
contour
of
the
left
ventricle
manually
(the
contour
is
shown
in
yellow) |
 | The
Endocardial
RV
contour
button
is
aimed
for
building
and
editing
the
inner
contour
of
the
right
ventricle
manually
(the
contour
is
shown
in
dark-blue) |
 | The
Epicardial
RV
contour
button
is
aimed
for
building
and
editing
the
outer
contour
of
the
right
ventricle
manually
(the
contour
is
shown
in
light-blue) |
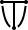 | The
LV
extension
boundaries
button
is
aimed
for
manual
determination
of
the
left
ventricle
extension
boundaries
along
the
long
axis
(see
Section 8.1.4) |
 | The
Auto
contouring
button
activates
the
process
of
automatic
contouring
of
the
left
ventricle
endocardium
end
epicardium
(see
Section 8.1.5) |
 | The
Contours
panel
button
is
used
to
expand/minimize
the
contours
panel
that
is
used
for
navigation
between
images
and
for
contour
management
(see
Section 8.1.7) |
 | The
Start
analysis
button
triggers
the
analysis
process
and
opens
a
panel
with
all
the
results
of
functional
parameters
evaluation
(see
Section 8.1.8) |
 | The
Edit
button
closes
the
panel
with
the
results
and
opens
the
toolbar
for
cardiac
function
analysis
to
provide
an
opportunity
to
build
and
edit
contours |
The functional parameters of the left and the right ventricles are calculated on the basis of the
contours built. Contours can be built separately for each slice and phase in the window with the SAX
merged series. The contour boundaries are shown as points on the slices in the window with the
merge LAX series. If two or more contours were built for one phase, the points can be
connected by segments. You cannot build contours in the window with a LAX merged
series.
To simplify the process of building contours, we recommend enabling the display of slices scout
lines in the window selected (see Section 2.26).
8.1.3 Building Contours Manually
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
You can use the following tools to build contours manually:
-
Endocardial LV contour  ;
;
-
Epicardial LV contour  ;
;
-
Endocardial RV contour  ;
;
-
Epicardial RV contour  .
.
The choice of the tool depends on the region of interest and the results of the analysis
required.
To build a contour, proceed as follows:
-
Open the study in the Cardiac analysis tab (see Section 8.1.1).
-
Activate one of the contour building tools with the left, right, or middle mouse button. To
continue work with the same tool, use the button with which the tool was activated. For
details on tool management, see Section 1.14. Build the contour in one of the following
ways:
-
building contours manually. In the window with the SAX merged series, build a
contour around the selected area while holding the button with which the tool was
activated. To complete the contour, release the mouse button. To cancel the contour
that has not been closed, click Esc on the keyboard while holding the mouse button;
-
building contours with an isoline. Move the cursor around the selected area
while holding the Shift button on the keyboard and the mouse button with which
the tool was activated. Under the cursor, you will see an isoline. You can see an
isoline only on the slices where a contour can be built. To build a contour with an
isoline, release the mouse button with which the tool was activated.
-
Go to the next slice and contour the selected area.
-
After you have built the required contours, click the Start analysis  button to go to the
results of parameters assessment (see Section 8.1.8).
button to go to the
results of parameters assessment (see Section 8.1.8).
If there is a contour built with the current tool on the current slice, you cannot build a new
contour here. You can only edit or delete the existing contour (see Section 8.1.6).
8.1.4 Evaluating the Left Ventricle Extension
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
To evaluate the left ventricle extension, you need the SAX and the LAX merged series to be
loaded to the Cardiac analysis tab (see Section 8.1.1).
To evaluate the left ventricle extension, proceed as follows:
-
Open the study in the Cardiac analysis tab (see Section 8.1.1).
-
Activate the LV extension boundaries  tool with the left, right, or middle mouse
button. To continue work with the same tool, use the button with which the tool was
activated. For details on tool management, see Section 1.14.
tool with the left, right, or middle mouse
button. To continue work with the same tool, use the button with which the tool was
activated. For details on tool management, see Section 1.14.
-
In the window with the SAX merged series, choose the slice for the upper plane of the
mitral valve and mark a point in the center of the mitral valve.
-
Go to the slice corresponding to the left ventricular apex and mark a point in the center
of the apex.
When you mouse over a point in the window with the SAX merged series, you see a pop-up tip
with the type of the point, Mitral or Apex.
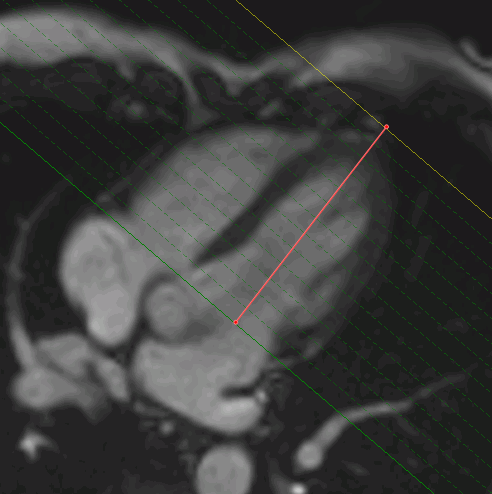
In the window with the LAX merged series, the left ventricle extension is marked with a line
(Fig. 8.5).
In multiphase series, the left ventricle extension may be determined for each phase.
8.1.5 Contouring the Left Ventricle Endocardium and Epicardium Automatically
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
In the Cardiac analysis tab, there are two options for automatic contouring:
For automatic contouring of the left ventricle endocardium and epicardium to be performed on
the slices for the selected phases, proceed as follows:
-
Open the study in the Cardiac analysis tab (see Section 8.1.1).
-
Determine the left ventricle extension (see Section 8.1.4) for the phases where the
contouring is to be performed.
-
Click the Auto contouring  button on the toolbar for cardiac function analysis.
button on the toolbar for cardiac function analysis.
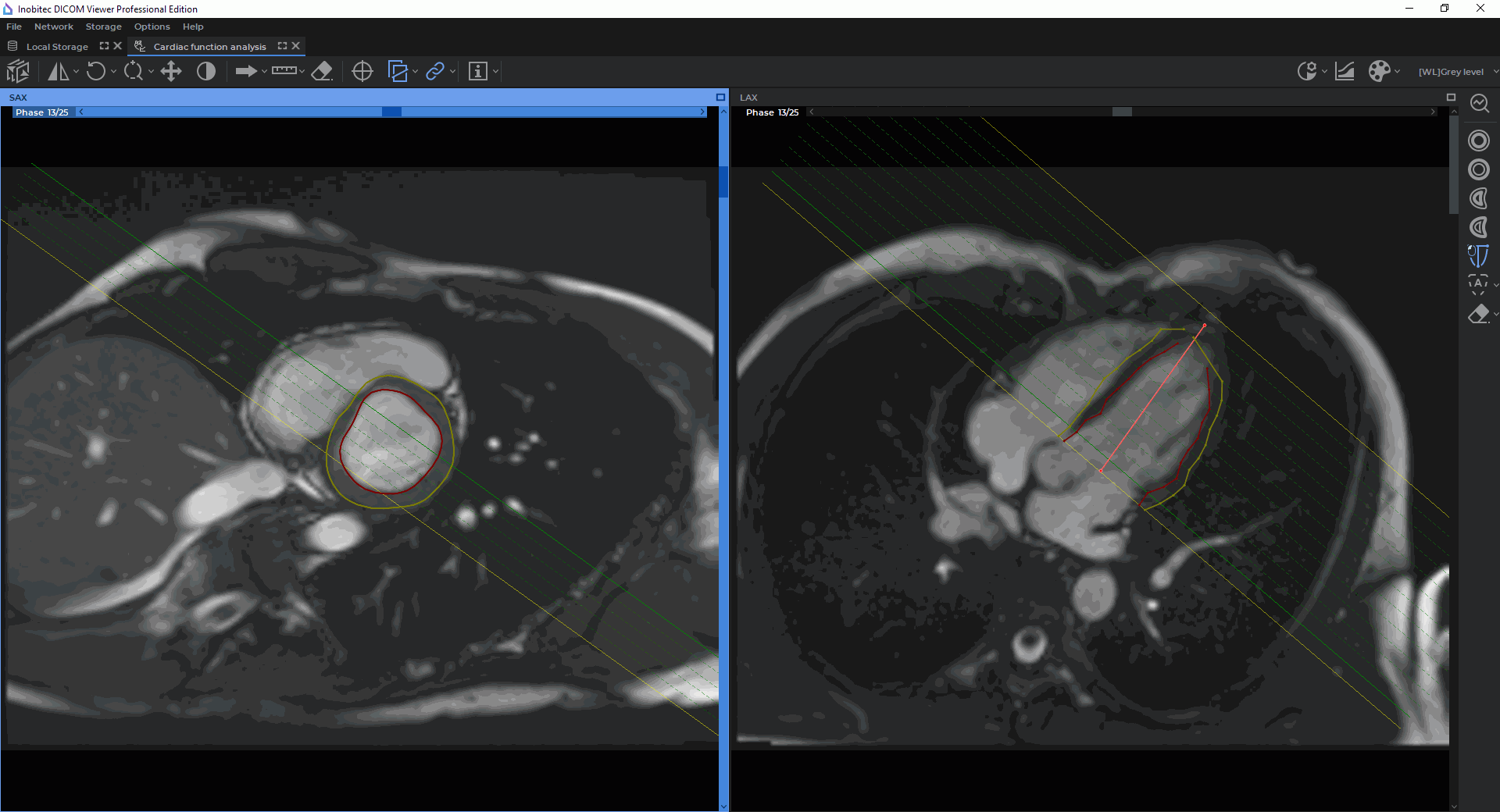
Automatic contouring of the left ventricle endocardium and epicardium are performed in the
window with the SAX merged series for all the phases with the left ventricle extension and all the
slices within the extension. The contour boundaries are shown on the slices in the window with the
LAX merged series (Fig. 8.6).
For automatic contouring of the left ventricle endocardium and epicardium to be performed on
the slices for all the phases, proceed as follows:
-
Open the study in the Cardiac analysis tab (see Section 8.1.1).
-
Determine the left ventricle extension (see Section 8.1.4) for the End Diastole (ED) and
End Systole (ES) phases.
 | If
the
number
of
phases
for
which
the
left
ventricle
extension
has
been
determined
does
not
equal
two,
automatic
contouring
for
all
the
phases
is
unavailable.
A
respective
warning
will
pop
up
on
the
screen. |
-
Click the arrow on the right-hand side of the Auto contouring  button and select
Build all contours based on two phases. The contouring process may take some
time.
button and select
Build all contours based on two phases. The contouring process may take some
time.
 | If
you
select
automatic
contouring
for
all
the
phases,
all
the
left
ventricle
contours
that
were
built
previously
will
be
deleted. |
Automatic contouring of the left ventricle endocardium and epicardium is performed in the
window with the SAX merged series for all the phases. The contour boundaries are shown on the
slices in the window with the LAX merged series (Fig. 8.6).
 | Attention!
If
a
part
of
the
atrium
is
present
on
the
mitral
valve
slice,
it
may
be
captures
while
contouring. |
To rebuild all the contours, press the arrow on the right-hand side of the Auto contouring  button and select Rebuild contours.
button and select Rebuild contours.
 | During
automatic
contouring,
it
is
possible
that
tissues
may
be
captured
by
the
contour
in
error.
Check
that
the
contours
are
drawn
correctly
and
edit
the
contours
manually
if
necessary. |
To go to the results of parameters assessment, click the Start analysis  button (see
Section 8.1.8).
button (see
Section 8.1.8).
8.1.6 Actions with Contours
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
The DICOM Viewer provides an opportunity to perform the following actions with contours in
the SAX window:
-
editing. Mouse over the selected contour. When the cursor is placed on the contour,
the contour is highlighted. Click the mouse button in the place where you want to edit
the contour and build a new contour while holding the mouse button. To complete the
contour, release the mouse button;
-
deleting a contour. Mouse over the selected contour, click the right mouse button, and
select the Remove contour option on the context menu;
-
deleting the extension boundaries. Place the cursor on one of the points used for
evaluating the LV extension. The point will be highlighted. Click the right-hand mouse
button and select the Remove extension boundaries option on the context menu.
Contours and LV extension boundaries can also be deleted from the contours panel (see
Section 8.1.7).
8.1.7 Contours panel
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
The contours panel (Fig. 8.7) is expanded/minimized with the "Contours panel"  button
on the cardiac analysis toolbar. By default, the contours panel is expanded.
button
on the cardiac analysis toolbar. By default, the contours panel is expanded.
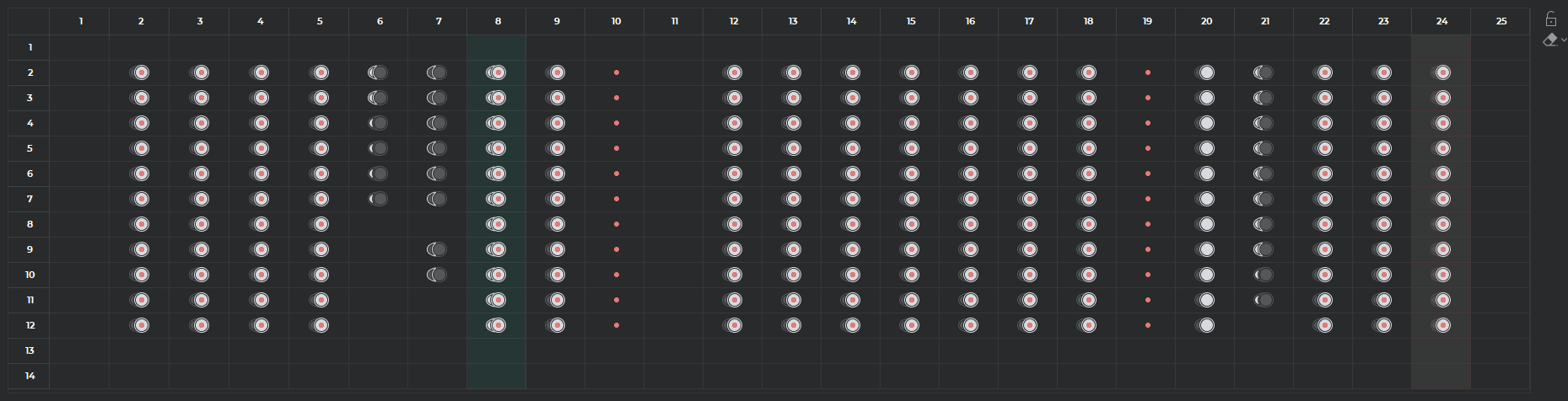
The contours panel provides for navigation between images and for contour management. The
contours panel is presented as a phase and slice contingency table. The column header shows the
phase number, and the line header shows the slice number. The cells contain information on contours
and LV extension boundaries in the form of conventional signs:
-
endocardial LV contour is  ;
;
-
epicardial LV contour is  ;
;
-
endocardial RV contour is  ;
;
-
epicardial RV contour is  ;
;
-
LV extension boundaries passage through the slice is  .
.
To go to the selected slice image and phase in the SAX window, left-click on the respective cell.
The cell corresponding to the image in the SAX window is highlighted.
The DICOM Viewer provides an opportunity to perform the following actions with
contours:
-
Deleting contours on the selected slice. Right-click on the selected cell and on the context
menu, select:
-
Remove LV endocardial contour (<slice number; phase number>);
-
Remove LV epicardial contour (<slice number; phase number>);
-
Remove RV endocardial contour (<slice number; phase number>);
-
Remove RV epicardial contour (<slice number; phase number>).
-
Deleting a certain type of contours on all the images for the selected phase.
Right-click on the column header (phase number) and on the context menu, select:
-
Remove LV endocardial contours (<phase number>);
-
Remove LVepicardial contours (<phase number>);
-
Remove RV endocardial contours (<phase number>);
-
Remove RV epicardial contours (<phase number>).
In the dialog box that opens, click YES to confirm the deletion, or click NO to
cancel.
-
Deleting a certain type of contours on all the images for the selected slice. Right-click
on the line header (slice number) and on the context menu, select:
-
Remove LV endocardial contours (<slice number>);
-
Remove LV epicardial contours (<slice number>);
-
Remove RV endocardial contours (<slice number>);
-
Remove RV epicardial contours (<slice number>).
In the dialog box that opens, click YES to confirm the deletion, or click NO to
cancel.
-
Deleting all the contours of the same type. Click the arrow on the right-hand side of the
Remove all cardiac contours  button. On the menu, select the type of contours you
want to delete from all the slices. In the dialog box that opens, click YES to confirm the
deletion, or click NO to cancel. The selected contour type is removed from all slices and phases
in the SAX window.
button. On the menu, select the type of contours you
want to delete from all the slices. In the dialog box that opens, click YES to confirm the
deletion, or click NO to cancel. The selected contour type is removed from all slices and phases
in the SAX window.
-
Deleting all the contours. To delete all the contours, click the Remove all cardiac
contours  button. In the dialog box that opens, click YES to confirm the deletion, or
click NO to cancel. All the contours on all the slices in the window with the SAX merged series
will be deleted.
button. In the dialog box that opens, click YES to confirm the deletion, or
click NO to cancel. All the contours on all the slices in the window with the SAX merged series
will be deleted.
-
Deleting LV extension boundaries for the selected phase. Right-click on the column
header (phase number) and on the context menu, select: Remove lv extension boundaries
(<phase number>).
The program automatically detects and highlights the end phases with the maximum and the
minimum ventricle cavity volume at the time of relaxation (diastole) and contraction (systole). The
final phase of contraction (ES) is highlighted with green, and the final phase of relaxation (ED) —
with red.
To lock the end phases, click the Lock end phases  button on the contours panel. After
the end phases are locked, the button will take the shape of
button on the contours panel. After
the end phases are locked, the button will take the shape of  . In this case, the end phases cannot
be detected automatically after creating, editing, and deleting contours. To enable automatic
detection of the end phases, click the Unlock end phases
. In this case, the end phases cannot
be detected automatically after creating, editing, and deleting contours. To enable automatic
detection of the end phases, click the Unlock end phases  button on the contours panel. The
button will take the shape of
button on the contours panel. The
button will take the shape of  .
.
The user may manually set and lock the selected end phase as ES or ED. To do that, right-click on
the column header (phase number) and on the context menu, select Set <phase number> as ES
or Set <phase number> as ED.
8.1.8 Evaluating Functional Parameters of the Heart
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Functionality is available in a separate module which is activated in the Pro edition for an extra fee
____________________________________________________________________________________________
To evaluate functional parameters of the heart, proceed as follows:
-
Open the study in the Cardiac analysis tab (see Section 8.1.1).
-
Build the required contours manually or automatically (see Sections 8.1.3 and 8.1.5).
-
Click the Start analysis  button on the toolbar for cardiac function analysis.
button on the toolbar for cardiac function analysis.
The results of functional parameters evaluation and the information on the patient are
presented as a table. The following basic parameters for the left and the right ventricle are
evaluated:
-
EDV (end diastolic volume), the maximum ventricle cavity volume at the end of diastole,
measured in ml. To evaluate the parameter, you need to build the endocardial contours;
-
ESV (end systolic volume), the minimum ventricle cavity volume at the end of contraction
(systole), measured in ml. To evaluate the parameter, you need to build the endocardial
contours;
-
SV (stroke volume), the volume of blood ejected with each heart beat, measured in ml
and calculated by the SV = EDV — ESV formula. To evaluate the parameter, you
need to build the endocardial contours;
-
EF (ejection fraction), the percentage of blood ejected with each heart beat calculated
by the EF = SV/EDV formula. To evaluate the parameter, you need to build the
endocardial contours;
-
CO (cardiac output), the amount of blood pumped in a minute, measured in l/min by
the CO = SV * heart rate formula. To evaluate the parameter, you need to build the
endocardial contours and know the heart rate;
-
CI (cardiac index), the cardiac output related to the body surface area (BSA).
The parameter is measured in 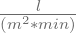 and calculated by the CI = CO/BSA
formula. The body surface area (BSA) is calculated by the following formula:
BSA = 0.007184 ∗ W0.425 ∗ H0.725, where W is the patient’s weight in kilos and H is
the patient’s height in centimeters. To evaluate the parameter, you need to build the
endocardial contours and know the patient’s weight and height;
and calculated by the CI = CO/BSA
formula. The body surface area (BSA) is calculated by the following formula:
BSA = 0.007184 ∗ W0.425 ∗ H0.725, where W is the patient’s weight in kilos and H is
the patient’s height in centimeters. To evaluate the parameter, you need to build the
endocardial contours and know the patient’s weight and height;
-
Myocardial mass, shows the difference in the epicardium and endocardium volumes at
the end of diastole (ED) and systole (ES) multiplied by a factor of 1.05, measured in g.
To evaluate the parameter, you need to build the endocardial and epicardial contours for
the ED and ES phases.
The results of functional parameters evaluation can be copied to the clipboard and then inserted
in the report editor (see Chapter 18) or in any text editor. To copy the results of functional
parameters evaluation to the clipboard, click the EXPORT TO CLIPBOARD button.
The coordinate system (Fig. 8.8) shows the functional parameters for all the phases as graphs. On
the x- axis, you can see the time in milliseconds while on the y- axis the blood volume is shown in
milliliters.
 | Attention!
Graphs
are
built
on
the
basis
of
the
contours
created
for
each
slice
of
each
phase
in
the
window
with
the
SAX
merged
series. |
The coordinate system shows the heart functional parameters as graphs:
-
left ventricle endocardium volume LV blood (red line);
-
left ventricle myocardium volume LV myocardial (yellow line);
-
right ventricle endocardium volume RV blood (dark blue line);
-
right ventricle myocardium volume RV myocardial (light blue line).
The measurement results are shown as a table on the right-hand side of the coordinate plane. The
values of the parameters reflect the measurement results for the current point.
The position of the current phase is marked with the yellow slider. To change the current phase on
the graph, mouse over the slider so that the cursor takes the  shape. Holding the left mouse
button, move the slider to the left or to the right. When you move the slider, the current phase in
the window with the SAX merged series is changed simultaneously. When the current
phase is changed, the measurement results shown in the table next to the graphs are also
changed.
shape. Holding the left mouse
button, move the slider to the left or to the right. When you move the slider, the current phase in
the window with the SAX merged series is changed simultaneously. When the current
phase is changed, the measurement results shown in the table next to the graphs are also
changed.
To move the graph along the y-axis, move the mouse up and down while holding the left mouse
button and the Shift key on the keyboard. To scale the graph, move the mouse up and down while
holding the left mouse button and the Ctrl key (or the Command key for macOS) on the
keyboard.
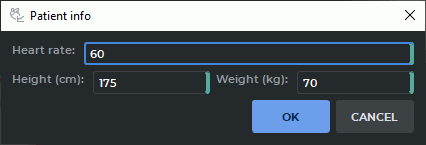
To edit the information on a patient, click the EDIT PATIENT INFO button and make the
necessary corrections in the dialog box (Fig. 8.9). Click OK to apply the new data or CANCEL to
cancel. After you click the OK button, the results of functional parameters analysis will be
reevaluated.
To get back to the contour building and editing mode, click the Edit  button.
button.
 button on the toolbar. To select the tab location (in
the current window, in a separate window, or in the full-screen mode), press the arrow
on the right-hand side of the button. To open the cardiac analysis window in a new tab
in the current window, press the button. The process may take some time.
button on the toolbar. To select the tab location (in
the current window, in a separate window, or in the full-screen mode), press the arrow
on the right-hand side of the button. To open the cardiac analysis window in a new tab
in the current window, press the button. The process may take some time.









 button. On the menu, select the type of contours you
want to delete from all the slices. In the dialog box that opens, click
button. On the menu, select the type of contours you
want to delete from all the slices. In the dialog box that opens, click  button on the contours panel. After
the end phases are locked, the button will take the shape of
button on the contours panel. After
the end phases are locked, the button will take the shape of  . In this case, the end phases cannot
be detected automatically after creating, editing, and deleting contours. To enable automatic
detection of the end phases, click the
. In this case, the end phases cannot
be detected automatically after creating, editing, and deleting contours. To enable automatic
detection of the end phases, click the 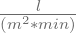 and calculated by the
and calculated by the 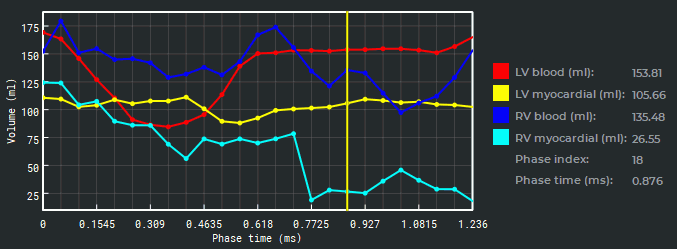
 shape. Holding the left mouse
button, move the slider to the left or to the right. When you move the slider, the current phase in
the window with the SAX merged series is changed simultaneously. When the current
phase is changed, the measurement results shown in the table next to the graphs are also
changed.
shape. Holding the left mouse
button, move the slider to the left or to the right. When you move the slider, the current phase in
the window with the SAX merged series is changed simultaneously. When the current
phase is changed, the measurement results shown in the table next to the graphs are also
changed.